molar conductivity table
Example 37 Use molar ionic conductivity data in Table 3-1 to calculate the mobility and diffusivity of Na Cl and NaCl at infinite dilution and 29815 K. Table 1 is a table of molar conductivity for the ions in this exercise.

Limiting Molar Conductivity K Diss And F For Polyelectrolytes Download Table
Aluminum chloride AlCl3 13334 6 3.

. High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 005 μScm at 25 C typical drinking water is in the range of 200800 μScm while sea water is about 50 mScm or 50000 μScm. Ity Λ which is the molar conductivity per unit concentration of charge is defined as Λ Λ Λ where Λ and Λ are equivalent ionic conductivities of the cation and anion. Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge.
If c is the solution in g molelitre then μ k 1000c. The ultrasonic velocities u for the estimation of isentropic compressibility were measured using a pulse echo overlap technique. 000061 10 6 cm Ω.
The customary unit is S cm 2 mol 1 ie Ω 1 cm 2 mol 1. In many cases conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids TDS. Ammonium bifluoride NH4FHF 5704 7 5.
Typical ranges for different electrolyte types are listed in Table 28. 10E-12 10 6 cm Ω. The first part of this table gives the molar conductivity of the hydrohalogen acids at 25 C as a function of the concentration in molL.
Pg292 Use the Henderson equation to estimate the liquid junction potentials for the following systems assume that the limiting molar conductivities given in table 62 can be used to calculate the ionic mobility. In the limit of infinite dilution non-interacting ions we obtain from Eq. The conductance is therefore 95010-4Scm.
S m 2 mol 1. Maximum conductance and Chemical point of inflection at 25C Mol. Contact Us Additional Resources.
2 EC0 i Λ0 mici F 2 RT i Diz2 i ci E C 0 i Λ m i 0 c i F 2 R T i D i z i 2 c i. Water Quality Conductivity Conversion Table Still have questions. Green numbers indicate high conductivity fluids suitable for magnetic flowmeters.
Acetic acid CH3COOH 185017 6005 2 2. AmmoniaAmmonium Hydroxide NH3NH4OH 120055 17033505 2 4. The molar conductivity is the conductivity of a solution for the ion containing one mole of charge per liter.
Ionic mobility Quantity defined by the velocity of an ion moving in. Table 1 gives the molar electrical conductivity of the hydrohalogen acids at 25 C as a function of the concentration. This table gives the molar equivalent electrical conductivity Λ at 25 C for some common electrolytes in aqueous solution at concentrations up to 01 M 01 molL.
Molar conductivities Λ M are normally determined using 1 10 3 M solutions of the complexes. Estimate the molar conductivity of 01 M HCl at 25C given that its limiting molar conductivity is 4262 cm mol and assuming an ionic size parameter a of 045 nm. It is given as.
It accounts for the obvious fact that ions with higher z are able to transport more charge. 10E-12 10 6 cm Ω. 80E-16 10 6 cm Ω.
The Molar conductance is described as the conductance of all ions produced by one mole of an electrolyte present in a fixed volume of the solution. This table presents the electrical resistivity and electrical conductivity of several materials. 10E-17 10 6 cm Ω.
The table below shows conversions between water conductivity and resistivity. The molar conductance of very dilute solutions 140 10 4 mol dm 3 was measured using a digital conductometer. Contact Aqua-Chem for Support.
The customary unit is S cm 2mol-1 ie Ω-1 cm2mol-1. Orange numbers indicate low conductivity and may not lead to successful applications. Conductivity Chart of Liquids conductivity too low for mag Low conductivity appl.
The more general formula is Λ Λ Λ v v where ν and ν refer to. Red numbers warn that conductivities are too low to use magnetic flowmeters. 20E-6 10 6 cm Ω.
Where V volume in mL having 1 g mole of the electrolyte. 000666 10 6 cm Ω. The molar conductivity SI units S cm2mol-1 is normalized for the concentration and is calculated as follows.
The equivalent conductivity refers to the normality of the solution rather than molarity. The ionic mobility is related to the molar ionic conductivity of the ion k. 145E-8 10 6 cm Ω.
Note that the molar conductivity of H ions is 5-7 times the conductivity of other small cations. It also converts resistivity to conductivity and to parts per million or milligrams per liter ppm mgL. The molar electrical conductivity Λ of an electrolyte solution is defined as the electrical conductivity divided by amount-of-substance concentration.
The lower the resistivity the more readily the material permits the flow of electric charge. In the realistic case of non-ideal solutions however the method becomes somewhat more. 7a a simple formula that relies on diffusion coefficients.
Molar conductivity ranges for different electrolytes ohm 1 cm 2 mol 1 at 25C. The molar conductivity Λ of an electrolyte solution is defined as the conductivity divided by amount-of-substance concentration. Name by Wt.
The molar conductivity of complex 2 of 536 ohm 1 cm 2 mol 1 indicated a 11 ratio between the complex and counterions whereas complex 3 had a molar conductivity of 184 ohm 1 cm 2. Electrical Conductivity Name Symbol 50E-24 10 6 cm Ω. Temp F µScm Acetaldehyde 59 17 Acetamide 212 43 Acetic Acid 03 644 318 1 584 5 1230 10 1530 20 1610 30 1400 40 1080 50 740 60 456 70 235 997 04 32 005.
The viscosities of the solutions were measured with an Ubbelohde suspended bulb viscometer. S cm 2 mol 1. Molar conductance μ k V.
The molar conductivity Λ m is defined as the conductivity of a 1 molar aqueous solution placed between two plates electrodes 1 cm apart. For very dilute solutions the molar electrical conductivity for any electrolyte of concentration c can be approximately calculated using the DebyeHückelOnsager equation which can. M L M 1000 Λ More explicitly Λ Λ 190 S cmmol There are three ions expected in solution CoH2O6NO32 CoH2O6 2aq 2 NO 3 - aq.
Conductivity molar ionic Magnetic field strength H Molar ionic conductivity A A. The molar conductivity of OH-is 3-5 times the conductivity of other. Graph Substance Formula µmhoscm by wt Anhydrous No.
Molar conductivity mol L 1 mol m 3 S cm 1. 228 rows There are 228 different materials listed in the conductivity table below. 252E-12 10 6 cm Ω.
Electrical resistivity represented by the Greek letter ρ rho is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current.

Molar Conductivity Measurements Data Download Table

Molar Conductances A And The Corresponding Concentration C Of Nai Download Table

Table Iii From Interactions Between Water And 1 Butyl 1 Methylpyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids Semantic Scholar

Equivalent Molar Conductivities And Corresponding Molarities Of The Download Table

Molar Conductivity Of Some Ions In Dilute Aqueous Solution At 25 C Download Table

Table 7 From Electrical Conductivity Of Electrolytes Found In Natural Waters From 5 To 90 C Semantic Scholar

Molar Conductivity At Infinite Dilution 0 M Of Kcl And Cacl 2 At Download Table
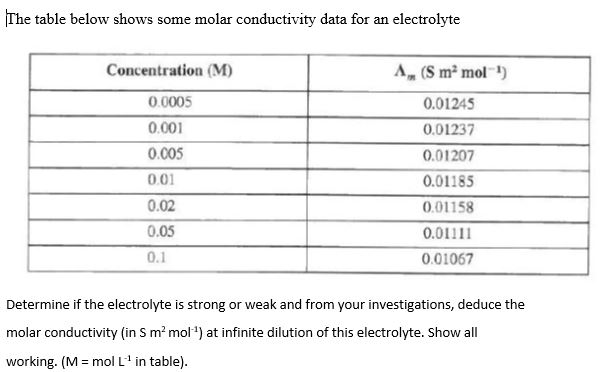
Solved The Table Below Shows Some Molar Conductivity Data Chegg Com

Values Of The Equivalent Conductance L S Cm 2 G Equiv 1 Of Na 2 Download Table

Equivalent Molar Conductivities And Corresponding Molarities Of The Download Table
Ionic Species Molar Conductivity Assignment Help

Elemental Analysis Colour And Molar Conductivity For Ligand And Its Download Table

Limiting Molar Conductance M For Nacl And Kcl In Aqueous Download Table

Molar Conductance M Of Nacl And Kcl In Aqueous Polyvinyl Alcohol Download Table

Molar Conductivity M Of Cacl 2 At Different Temperatures In 0 50 Download Table
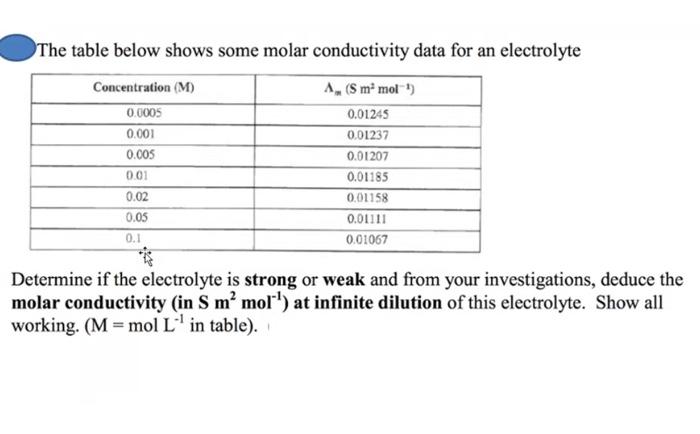
Solved The Table Below Shows Some Molar Conductivity Data Chegg Com

Molar Conductivity And Stokes Radii For Cations Used Download Table

Table 6 From Electrical Conductivity Of Electrolytes Found In Natural Waters From 5 To 90 C Semantic Scholar

Molar Ionic Conductivities Of Some Mono Charged Ions Download Table
Comments
Post a Comment